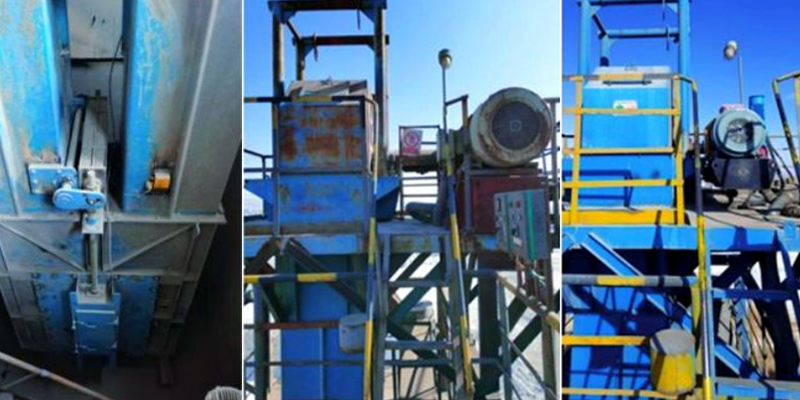
In the world of industrial bulk material handling, precision, reliability, and efficiency are paramount. Among the critical components that ensure these qualities, the slide gate valve stands out for its simplicity and effectiveness. This versatile device is a cornerstone in controlling the flow of dry bulk materials, from powders and pellets to granules and flakes. Understanding its operation, types, and applications is essential for optimizing any industrial process.
What is a Slide Gate Valve?
A slide gate valve is a linear motion valve used primarily to start, stop, or regulate the flow of dry bulk materials. Unlike butterfly or knife gate valves designed for liquids, a slide gate valve operates by moving a flat plate, or “gate,” linearly across the material stream. This gate slides into and out of the path of the flowing material, creating a tight shut-off or allowing for precise metering. Its robust and straightforward design makes it a preferred choice in industries like food processing, pharmaceuticals, plastics, and cement manufacturing.
Core Functions: What is a Slide Gate Used For?
The primary function of a slide gate valve is isolation, but its role extends to several critical operations:
-
Flow Isolation and On/Off Control: The most common use is to completely stop or allow material flow in a process line, acting as a reliable shut-off device.
-
Diversion: Specialized configurations, like double slide gate diverters, are used to direct material flow from one source to one of two different destinations.
-
Metering and Flow Control: While not as precise as a dedicated feeder, a flow control gate valve can be partially opened to throttle and regulate the volume of material discharge from bins, hoppers, or silos.
-
Airlock Integration: Often paired with a rotary airlock valve, the slide gate acts as an isolation device above the airlock, allowing for maintenance or creating a pressure differential in pneumatic conveying systems.
The Operating Mechanism: How Does a Slide Valve Work?
The working principle of a slide gate valve is elegantly simple, relying on a linear, sliding motion. Here is a step-by-step breakdown of its mechanism:
-
The Open Position: The valve’s gate plate is fully retracted from the valve body’s opening. This allows bulk material to flow freely through the valve unimpeded.
-
The Closing Action: An actuator (manual, pneumatic, or electric) moves the gate plate linearly across the flow path. The gate slides on a sealed surface, shearing through any material in its way and eventually closing the opening completely.
-
The Closed Position: The gate plate now fully obstructs the flow path, creating a seal that prevents material from passing through. This isolates the upstream equipment from the downstream process.
-
The Re-Opening Action: The actuator reverses the motion, retracting the gate plate back to its open position and re-establishing material flow.
The effectiveness of this mechanism depends on a tight seal between the gate and the valve body, which prevents leakage and ensures a positive shut-off.
Methods of Actuation: From Manual to Automated
Slide gate valves are categorized based on how the gate plate is moved, each offering distinct advantages for different applications.
| Actuation Type | How It Works | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Manual Slide Gate Valve | Operated by a handwheel, lever, or crank. | Low-frequency operations, remote locations without power, or applications with budget constraints. |
| Pneumatic Slide Gate Valve | Uses a pneumatic (air) cylinder to automate the sliding motion. | High-speed automation, harsh/dusty environments, and integrated process control systems. |
| Electric Slide Gate Valve | Uses an electric motor for actuation. | Applications requiring precise positioning for flow control and where compressed air is not available. |
| Screw Slide Gate Valves | A manual valve where a threaded screw mechanism advances the gate. | Applications requiring very fine control over the gate position for precise metering. |
Key Industrial Applications
The robustness of the slide gate valve makes it suitable for a wide array of industries:
-
Food & Beverage: Handling sugar, flour, grains, and spices. Valves are often manufactured with sanitary standards in mind.
-
Pharmaceuticals: Controlling the flow of powder ingredients and granules in tablet presses and mixers.
-
Plastics & Chemicals: Metering plastic pellets, resins, and various chemical powders in production and packaging lines.
-
Mining & Minerals: Managing the flow of abrasive materials like cement, sand, and ores from storage silos.
-
Energy: Handling fly ash and other combustion by-products in power generation facilities.
How to Select the Right Slide Gate Valve
Choosing the correct valve is critical for system performance and longevity. Consider these factors:
-
Material Characteristics: Analyze the bulk material’s properties, including abrasiveness, cohesiveness, particle size, and weight. Abrasive materials require hardened surfaces or specialized liners.
-
Process Requirements: Determine the primary need: simple on/off control, diversion, or precise flow regulation. This will guide you toward a standard valve, a double slide gate diverter, or a flow control gate valve.
-
Actuation Method: Decide between manual, pneumatic, or electric actuation based on required speed, frequency of operation, and available plant utilities.
-
Size and Pressure: Ensure the valve size matches your pipeline or outlet dimensions and that it is rated for the system’s pressure and temperature.
-
Quality and Supplier: Source your valves from reputable slide gate valve manufacturers who can provide technical support, custom solutions, and quality assurance.
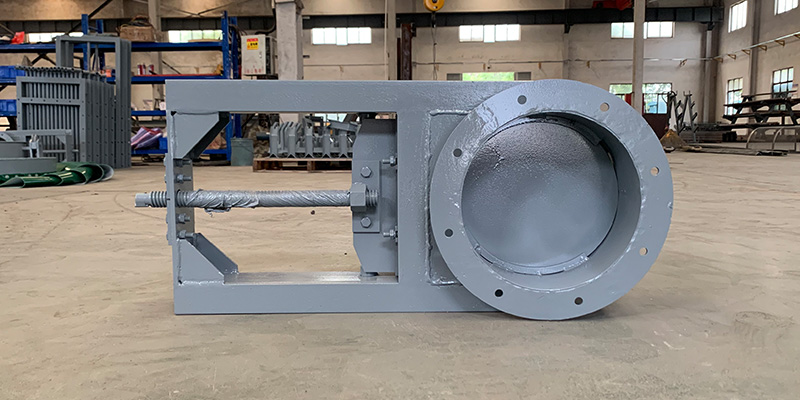

Advantages Over Alternative Valves
Why choose a slide gate valve over other types like butterfly or knife gate valves?
-
Full, Unobstructed Flow: In the open position, the gate is completely out of the flow path, minimizing pressure drop and preventing material buildup.
-
Excellent Shut-Off: Provides a tight seal, ideal for handling fine powders that can leak through other valve types.
-
Durability and Low Maintenance: Its simple design has fewer moving parts, making it robust and easy to maintain.
-
Versatility: Available in various sizes, materials of construction, and actuation methods to suit nearly any application.
-
Abrasion Resistance: The linear sliding motion is often less damaging to the valve seat than the rotational motion of a butterfly valve, especially when handling abrasive materials.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What is the main difference between a slide gate valve and a rotary airlock valve?
A slide gate valve is primarily used for isolation and on/off control, stopping material flow entirely. A rotary airlock valve, with its rotating vanes, is designed to meter material at a consistent rate while also acting as an airlock to maintain pressure differentials in pneumatic systems. They are often used together.
Q2: Can a slide gate valve be used for both powder and pellet materials?
Yes. The design can be tailored to handle both. For powders, a tighter seal and potentially a soft seat are used to prevent leakage. For pellets, a more durable, hardened gate might be specified to withstand impact and abrasion.
Q3: What are the advantages of a pneumatic slide gate valve?
The pneumatic slide gate valve offers rapid operation, remote control capability, and is ideal for integration into automated and safety-interlocked systems. It is also well-suited for explosive or dusty environments where electric sparks are a concern.
Q4: How do I maintain my slide gate valve?
Regular maintenance involves inspecting the gate and body for wear, especially from abrasive materials, and checking the seals for integrity. Keeping the sliding surfaces clean and ensuring the actuator functions smoothly will significantly extend the valve’s service life.
Conclusion
The slide gate valve is an indispensable workhorse in dry bulk material handling. Its straightforward sliding mechanism, combined with a range of actuation methods and robust designs, provides a reliable solution for isolation, diversion, and control. By carefully considering material properties, process needs, and actuation requirements, you can select the ideal slide gate valve to enhance the efficiency, safety, and reliability of your operations.