In cement production and transport, clogging is a common problem. Moisture and natural conditions make cement form hard lumps inside storage silos. These lumps severely block discharge channels. As a result, loading time can increase from 15 minutes to over an hour. This also causes false flow signals, process issues, and even equipment failure. So, how can we solve this problem efficiently and cleanly? The Cement Lump Breaker Valve is the key solution. This article will explain its functions, working mechanism, advantages, and how to choose the right one. It will help you say goodbye to clogging for good.
Why You Need a Lump Breaker ?
The main job of a cement lump breaker is simple. It breaks lumps in the material flow from the discharge feeder. This action ensures continuous and stable material handling.
-
It Solves Root Cause Blockages: Cement often forms large, hard lumps inside silos due to moisture. These lumps cannot pass through the small outlet of the discharge feeder. They are the main cause of material blockages.
-
It Eliminates False Signals for Safety: Blocked material makes flow control valves send incorrect signals. This lightly disrupts normal production. In serious cases, it causes a severe imbalance in the raw material and fuel ratio. Consequently, temperatures in the combustion equipment can become too high and cause accidents.
-
It Boosts Loading Speed and Satisfaction: Clogging can reduce loading efficiency by over 80%. Loading times stretch from minutes to hours. This directly leads to more customer complaints and harms the company’s image and competitiveness.
Imagine this: A system without a breaker valve is like a highway constantly blocked by boulders. The breaker valve is the efficient, tireless tow truck that keeps the traffic flowing smoothly.
How It “Breaks” the Problem?
The cement lump breaker has a smart and efficient design. Its work process is an intelligent loop of detection, breaking, and self-protection.
1. Drive and Breaking Mechanism
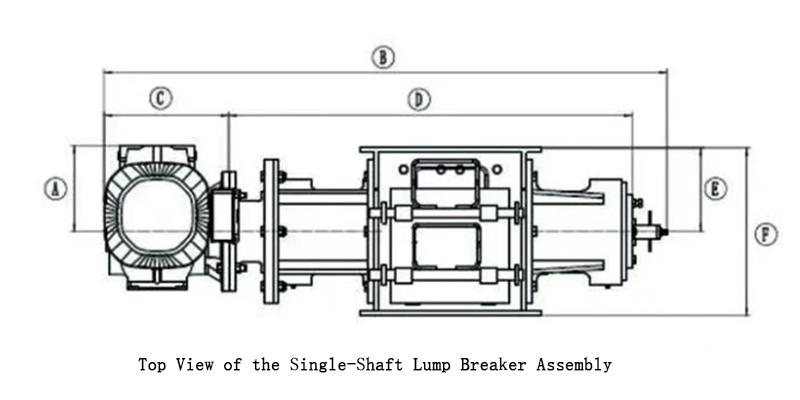
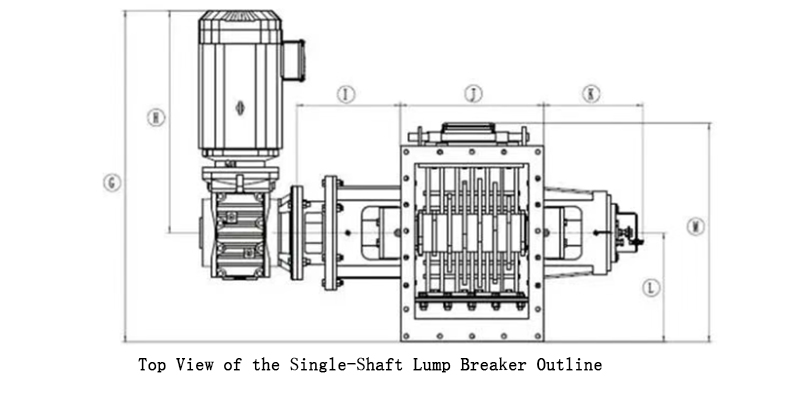
The breaker usually uses an electric motor. Its core structure includes:
-
A Housing: This forms the main body. It has a top inlet and a side outlet.
-
A Rotor System: Inside the housing, two parallel rotors are placed. A motor and gear reducer power them. A drive gear on the main rotor meshes with a gear on the second rotor. This makes them rotate toward each other.
-
Breaking Elements: Both rotors have radiating breaking claws (or rotating blades). These claws are made of high-wear-resistant material. They interlock and create a powerful shearing and crushing action.
Work Process: Material enters the housing. Lumps are caught by the high-speed rotating claws. The claws shear, impact, and crush the lumps until they are small enough to pass through the grid plate. Finally, the material exits from the outlet.
2. Smart Safety Protection Mechanism
Advanced breakers have intelligent control systems for self-protection. This handles extreme situations.
-
Speed Monitoring Device (Optional): A sensor in the control cabinet monitors the rotor speed in real-time.
-
Auto-Reverse and Alarm: If an unbreakable lump jams the rotor, the device alarms immediately. It then commands the motor to reverse automatically. This tries to push the lump away. After that, the device returns to forward rotation.
-
Repeated Attempts and Final Shutdown: If the lump is too hard, the device cycles through “forward-reverse” motions several times. If it still fails, or if the rotor jams instantly in both directions, the system shuts down automatically. It then waits for manual intervention. This prevents damage to the equipment.
This mechanism greatly improves automation and operational reliability. It also reduces the need for risky manual maintenance.
Key Advantages: Why Choose It?
Compared to manual cleaning or simple methods, the cement lump breaker offers multi-dimensional value.
-
High-Efficiency Breaking: The interlocking multi-rotor design ensures high breaking efficiency. It quickly processes lumps and ensures smooth material flow. This restores loading speed to normal levels.
-
Full Automation: It enables unmanned operation. This completely eliminates the need for workers to enter confined and dangerous spaces for manual cleaning. It also reduces labor intensity.
-
Better, Cleaner Work Environment: The device uses multiple sealing points. This effectively prevents cement dust from escaping. Therefore, it reduces environmental pollution and health risks for operators.
-
Easy Maintenance and Durability: Key wear parts like breaking claws and grid plates use high-wear-resistant materials. This gives them a long service life. Modular design also makes daily checks and part replacement easier.
-
Protects the Entire Process System: By eliminating blockages and false signals, it protects downstream equipment like flow valves and burners. This ensures the stability and safety of the whole system.
Wide Application and Flexible Installation
The cement lump breaker is highly adaptable. It is an ideal solution for many scenarios.
-
Main Application Scenarios:
-
Cement silo dust discharge systems.
-
Discharge outlets for various fluidized sloping channels.
-
Discharge points for powder or fine particle storage silos.
-
-
Installation Methods:
-
It supports both horizontal and vertical installation. This offers great flexibility.
-
You usually install it at the inlet end of discharge equipment (like flow control valves or pneumatic shut-off valves). It acts as a “goalkeeper.”
-
See the table below for a clearer view of its strong adaptability across different scenarios.
| Application Scenario | Problem It Solves | Installation Advice |
|---|---|---|
| Cement Silo Discharge | Slow loading and clogging from cement lumps | Install vertically above the loading spout, or horizontally in the conveyor pipeline |
| Fly Ash / Slag Powder Silo | Bridging and clogging from hygroscopic powders | Install at the silo discharge outlet to ensure powder flows into conveying equipment |
| Under Raw Mix Homogenizing Silo | Lumps from uneven material moisture | Install before pneumatic shut-off valves to protect these precise valves |
| Pneumatic Conveying System | Pipe clogging and pump damage from lumps | Install after the feed inlet of the sending tank, as the final safeguard before material enters the pipeline |
How to Choose the Right Lump Breaker
Selecting the right breaker valve is key to ensuring a good return on your investment. Please see the decision matrix below.
| Selection Factor | What to Consider | Suggestion |
|---|---|---|
| Material Properties | Material type, moisture level, lump hardness and size | Choose claw material and wear resistance based on lump hardness |
| Flow Requirements | Maximum and average handling flow (m³/H) | Select a model with a capacity slightly above your system’s max flow (Largest model reaches 1000 m³/H) |
| Working Environment | Material temperature, environmental corrosiveness | Ensure the device’s design temperature (e.g., up to 120°C) meets your needs. Choose special coatings if necessary |
| Automation Needs | Need for unmanned operation and auto-protection | We strongly recommend selecting the “Speed Monitoring Device”. It enables auto-reverse, alarm, and shutdown |
| Installation Space | Pipeline layout and space limits | Choose horizontal or vertical models based on available space |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: How is a Cement Lump Breaker different from a regular valve?
A: Regular valves (like gate valves or butterfly valves) mainly “start/stop” or “control” flow. A lump breaker is a power device. Its core function is to actively “break” and “crush” lumps in the material. Think of it as a compact crusher built into your pipeline.
Q2: Can the breaker valve be used for mixing or conveying other materials?
A: No. The breaker valve is designed specifically for breaking lumps and ensuring flow. It targets the unwanted “lumps” in the material. Its purpose is not to mix materials evenly like a mixer, nor to provide conveying power like a conveyor.
Q3: Besides cement, what other industries can use it?
A: Absolutely. It applies to any industry handling powders or fine granules that easily absorb moisture and form lumps. Examples include: fly ash, slag powder, raw meal powder, grains, animal feed, and chemical powders in their storage and handling systems.
Q4: Is the optional Speed Monitoring Device necessary? What is its main advantage?
A: It is not mandatory, but we highly recommend it. Its core advantage is intelligent protection. It not only automatically handles minor jams to prevent stoppages but also protects the motor and drive system from damage when it meets unbreakable objects. It does this through alarms and automatic shutdown. This prevents small issues from causing major repairs, offering high long-term value.