01.The Current Situation and Renovation Plan of the Hoist
►types of bucket elevator and Advances in wire belt
The bucket elevator plays a crucial role in the vertical transportation in HuaXin cement. There are various types of bucket elevators. Among them, wire belt bucket elevator and chain bucket elevator are two main types. In the past, due to the impact of material temperature on the traction components, high-temperature materials (such as cement discharged from mills and slag from vertical mills, exceeding 110°C) were typically transported using chain elevators.
However, with the continuous advancement of wire belt technology, its temperature resistance has significantly improved. This allows the wire belt bucket elevator to withstand high temperatures of up to 130°C for long periods, and even reach 150°C for short durations. Additionally, wire belt bucket elevators offer numerous advantages, including high efficiency, low weight, low energy consumption, and low maintenance costs.
As a result, we usually choose wire belt bucket elevators in processes such as discharging cement fom mill, recovering heat for power generation, and transporting mixed materials. The wire belt bucket elevators are increasingly demonstrating their technical advantages over chain bucket elevators.
►Problems with the bucket elevator before the renovation
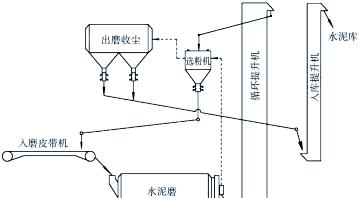
The #1 cement grinding system at a cement plant was originally equipped with a chain bucket elevator. The chain bucket elevator was responsible for elevating the discharged cement form mill to separator for further processing. However, several issues were exposed before the renovation:
- Material Leakage: There were frequent occurrences of material leakage and oil leakage from chain bucket elevator tail. This resulted in severe accumulation of materials in the tail pit, worsened the working environment, and increased the maintenance workload.
- Heavy Components: The heavy weight of chains and buckets led to relatively high energy consumption for the entire system.
- Rapid Wear of Chains: During actual operation, the chains experienced excessive and uneven wear, resulting in a high consumption of spare parts. This not only posed challenges to the safe and stable operation of the equipment but also directly affected the continuous production of the grinding system.
02 Modification and implementation
► Main modification measures
After comprehensive research and assessment, we decided, accordingly, to meet the on-site production demands by retaining the original exterior shell and maintenance platform. We will only replace the conveying components, tail tensioning device, built-in tailwheel, headwheel assembly, and head drive. By implementing targeted upgrades to these conveying parts, as well as the tail and head, we successfully completed the technological enhancement.
► Details of the conveying component
We completely removed the original conveying components, such as chains and buckets, and replaced them with high-performance wire belts and compatible buckets. Special attention was given to the selection of the wire belt, as it is the core component of the belt bucket elevator. The wire belt must maintain safety performance in high-temperature, high-load, and high-speed cyclic operation environments, necessitating exceptional temperature resistance, tear resistance, high fatigue strength, and low elongation.
We selected an exclusive Type II heat-resistant wire belt, which ensures strength and tear resistance while also providing superior temperature resistance, capable of with standing material temperatures of ≤120℃ over extended periods, and even reaching 150℃ momentarily. Additionally, the specialized alloy belt clips and dedicated adhesive locking technology ensure that the joint strength of the wire rope belt is comparable to the strength of the belt itself, thereby guaranteeing the long-term safe and reliable operation of the bucket elevator.

► Tail modification
- Tensioning Device Innovation: We abandoned the original external spring tensioning device and introduced a four-bar parallel guiding tensioning mechanism. This new mechanism consists of a four-bar axis, rocker arms, and a counterweight, forming a parallel sliding frame. When the tailwheel moves up and down due to applied force, the rocker arms on both sides of the four-bar assembly swing in unison, ensuring that both ends of the tailwheel rise and fall synchronously. Additionally, the clever design of limit guides and bearing seat limit rails effectively prevents axial movement of the tailwheel, achieving automatic synchronous tensioning.
(2) Improvements to the Tailwheel Assembly and Maintenance Door: We removed the original tail sprocket, external partitions, maintenance door, and bearing seat, replacing them with a better-sealed built-in tailwheel. Furthermore, we replaced it with an integrated maintenance door for the tail section. The new tailwheel is designed in a rod-shaped, cage-like structure, machined with a special arc for automatic alignment, ensuring concentricity. Its anti-jamming design features a dual-cone material discharge system, effectively preventing material accumulation between the tailwheel and the belt, thereby reducing wear on both the tailwheel and the belt.
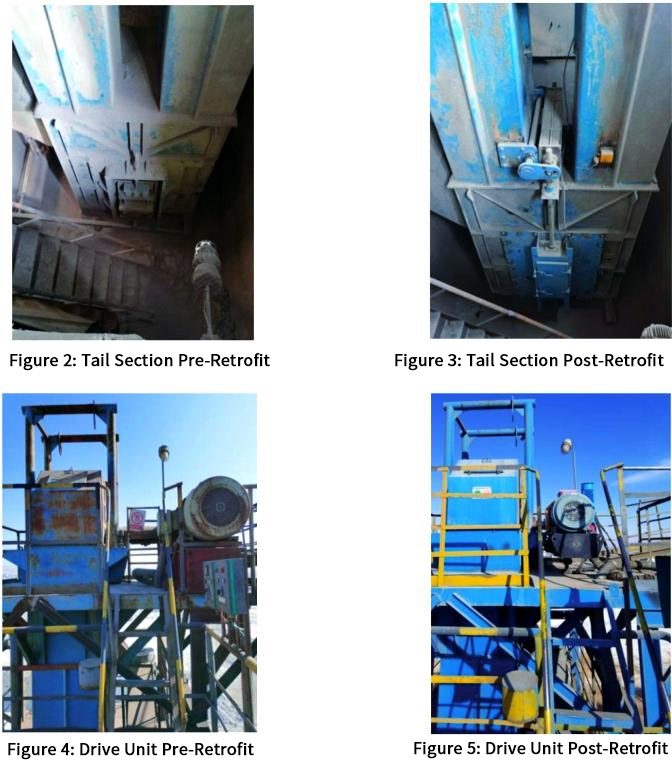

► Head modification
We completely removed the original head components, including the 132 kW motor, matching reducer, fluid coupling, sprocket assembly, and drive bracket. Subsequently, we installed a new 55 kW motor along with its compatible reducer and magnetic coupling drive system.
The design of the new drive bracket employs a torsion arm suspended cantilever mechanism, which is connected to transverse channel steel. After careful adjustment and assembly to ensure the precision of all components, we securely fixed the channel steel in the appropriate position beneath the original maintenance platform.
► Installation of control components
During the renovation process, we not only conducted a comprehensive upgrade of the head components but also installed various monitoring elements, including material level sensors, misalignment switches, and speed sensors.
Notably, the misalignment switch features an innovative external assembly design, with key components such as the sensor cleverly positioned outside the housing. This design aims to enhance the reliability of the device in actual use.
03Transformation Results and Conclusions
► Comparison of renovation effects
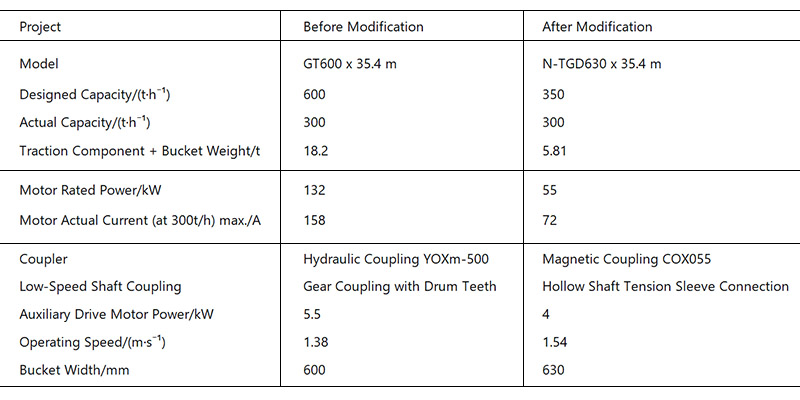
After comprehensive upgrades and careful modifications, the performance parameters of the bucket elevator have significantly improved. The actual energy consumption after the renovation has been greatly reduced. In particular, the use of the Type II heat-resistant wire rope belt allows the wire rope belt elevator to better adapt to the working environment on-site.
| Item | before innovation | after innovation |
| Type | GT600 x 35.4 m | N-TGD630 x 35.4 m |
| Design Capacity (t/h) | 600 | 350 |
| Actual Capacity (t/h) | 300 | 300 |
| traction elements and buckets weight (t) | 18.20 | 5.81 |
| Motor rated power (kw) | 132 | 55 |
| Actual current of the motor at 300t/h (max/A) | 158 | 72 |
| Coupler | fluid coupling YOXm-500 | magnetic coupling COX055 |
| Low-speed shaft coupling | curved tooth coupling | Hollow shaft tensioning |
| Auxiliary transmission motor power (kw) | 5.5 | 4 |
| Running speed (m/s) | 1.38 | 1.54 |
| Bucket width (mm) | 600 | 630 |
► Summary
The renovation project was carried out while retaining the original shell, with no modifications made to key components such as the inlet and outlet, maintenance platform, equipment foundation, pit, and the shell’s support frame. This approach not only saved significant time and investment costs but also ensured the stable operation of the equipment.
Since the completion of the renovation, the equipment has been running steadily, with a clean and orderly on-site environment. Daily maintenance work primarily focuses on regular inspections and lubrication of key areas such as joints and various lubrication points, resulting in a low overall workload. All performance indicators have met the expected targets.